An enterprise service bus enables applications to communicate with each other. Learn how it works, and how we're using it at UCLA.
An Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) is a type of software platform known as middleware, which works behind the scenes to aid application-to-application communication. Think of an ESB as a “bus” that picks up information from one system and delivers it to another.
The term ESB first appeared in 2002, but the technology continues to evolve, driven by the need for ever-emerging internet applications to communicate and interact with one another.
Why would I want an ESB?
Imagine that there are two systems in an organization that need to exchange data. The technical teams that represent each system plan and implement a solution that allows these systems to communicate. A year or two later, the organization deploys several more systems that need to interact with each other as well as the existing two systems. How can all teams develop and reach agreement on the best solution?
It becomes very complicated to manage and maintain one solution as an organization’s IT systems expand. With just 10 systems, there could be 100 different interfaces and scores of disparate technical requirements.
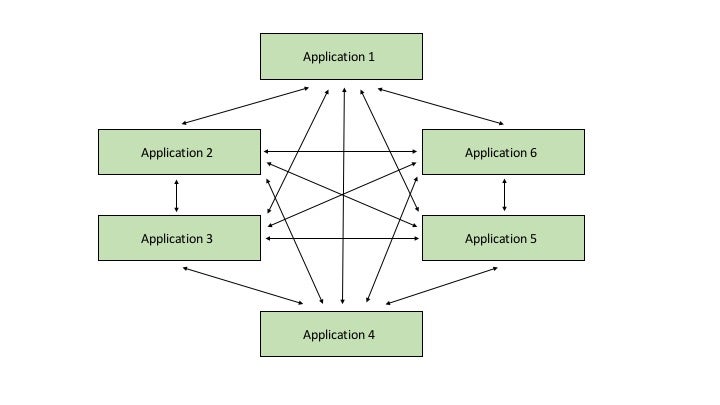
ESB is the Solution
An ESB provides a secure, scalable and cost-effective infrastructure that enables real-time data exchange among many systems. Data from one system, known as a service provider, can be put on the enterprise service bus as a message, which is sent immediately to a service consumer of the data. If a new system wants to consume this same data, all it has to do is plug into the bus in the same manner.
An ESB can provide
- Messaging (asynchronous): Exchange data in real-time among systems.
- Web Services (e.g., SOAP & REST): Use applications that broker data requests and delivery.
- Data Transformation (e.g., XML, XSLT, JSON): Transform the data format to meet your system’s needs, or to add value to the data you receive.
- Routing Intelligence: Get secure access control to services and intelligent routing of data along its intended path.
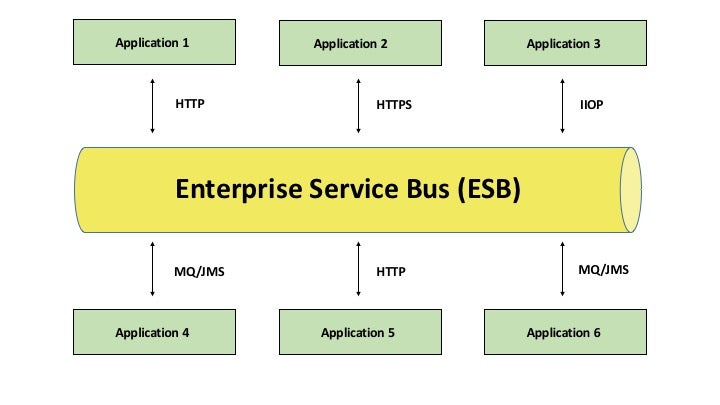
The UCLA ESB
The UCLA ESB has been in operation since 2014 and is based on Red Hat JBoss Fuse. Although UCPath was the initial driver for its creation, the UCLA ESB is a shared platform available to the entire campus. It’s currently being used by several campus departments, including UCLA Financial Systems and Student Affairs.
To learn more about the UCLA ESB visit the ESB Wiki.


